India’s economy continues its trajectory as one of the fastest-growing in the world, and Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) are taking note. While residential property has long been the default investment choice, a significant shift is underway. The spotlight is now firmly on commercial real estate in India, an asset class that consistently delivers superior rental yields and robust capital appreciation. The prospect of investing in Grade-A office spaces, high-street retail, and modern warehousing from thousands of miles away is not just a dream—it’s a viable, profitable strategy.

This comprehensive guide is designed for the senior investor like you. It cuts through the complexities of cross-border transactions, simplifies the regulatory maze, and lays out an actionable roadmap for successfully acquiring commercial property without having to be physically present. Buying commercial real estate in India remotely is entirely possible, provided you follow a structured, legally compliant, and diligently planned process. We’ll show you exactly how to transform this lucrative opportunity into a cornerstone of your wealth portfolio.
Why Commercial Real Estate in India is a Magnet for NRIs
The decision to invest in commercial assets over residential ones is driven by fundamental economic principles. The Indian commercial property sector is far more resilient to market fluctuations and offers several distinct advantages that appeal directly to the sophisticated NRI investor focused on cash flow and long-term security.
Firstly, the most compelling factor is the higher rental yield. While typical residential properties in major Indian metros offer annual rental returns of 2-3%, prime commercial properties often command yields in the range of 6-10%, with some retail and industrial assets going even higher. This stable, high-yield passive income is critical for portfolio diversification. Commercial leases are also generally structured for the long term, often spanning three to nine years with built-in escalation clauses, providing predictable income growth. This stability contrasts sharply with the shorter, often volatile tenures of residential rentals.
Secondly, India’s economic growth is heavily dependent on corporate expansion and consumption, directly fueling the demand for new office, retail, and logistics space. As multinational companies (MNCs) and domestic giants expand, they require premium office space in metropolitan hubs like Bengaluru, Mumbai, Pune, and Hyderabad, driving up both rents and property values. Investing in these key business districts is essentially a bet on India’s sustained corporate growth. Finally, the regulatory environment is more transparent than ever before, thanks to the introduction of the Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act (RERA) and the increasing formalization of the sector. This governance boosts NRI confidence in undertaking cross-border investments in commercial real estate in India.
Navigating the Legal & Financial Landscape: The NRI’s Playbook
For an NRI, the initial hurdle is often the perception of a complex legal and financial framework. It’s vital to demystify these regulations, as adherence is the bedrock of a secure investment. A successful strategy for buying commercial real estate in India remotely starts here.

Understanding FEMA and RBI Regulations
The primary legislative framework governing NRI investment in India is the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999, monitored by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). The good news is that, under FEMA, NRIs have general permission to purchase residential or commercial property. No prior approval from the RBI is required to buy or sell these types of properties. This is a significant relaxation that simplifies the investment process considerably.
However, there are restrictions: NRIs are prohibited from purchasing agricultural land, plantation property, or farmhouses, though they may inherit them. Furthermore, all financial transactions related to the purchase—from the initial booking amount to the final payment—must be routed through official banking channels. This means funds must come from inward remittances from abroad or by debiting your Non-Resident External (NRE), Non-Resident Ordinary (NRO), or Foreign Currency Non-Resident (FCNR) accounts. Strict adherence to these rules ensures the investment is compliant and sale proceeds can be repatriated in the future.
Bank Accounts and Funding Your Commercial Real Estate Purchase
To successfully invest, you must have the right bank accounts set up. Your NRE account is crucial for repatriating your foreign earnings to India; funds held here are freely and fully repatriable abroad. The NRO account, conversely, is where income earned in India—like the rental income from your commercial property—is deposited. Funds in the NRO account are generally not fully repatriable, though you can transfer up to USD 1 million per financial year (after taxes) from your NRO account to your NRE account or directly abroad.

For the purchase itself, all payments must be made in Indian Rupees (INR). You can use a combination of funds from inward remittance or by debiting your NRE/NRO/FCNR accounts. Securing an NRI home loan is also an option, with many major Indian banks offering competitive commercial property loan products. These loans are also repaid in INR, typically debited automatically from your NRE or NRO account. Properly documenting the source of funds is paramount for future tax and repatriation ease after the sale of the commercial real estate in India.
The Critical Role of Power of Attorney
Since you are undertaking the investment remotely, a Power of Attorney (PoA) is an indispensable tool. A PoA legally grants a trusted individual (your representative or a professional legal counsel) the authority to act on your behalf for specific tasks, such as signing the sale agreement, coordinating with the developer, engaging in loan documentation, and completing the final registration.
The PoA document must be carefully drafted to be specific and limited to the property transaction, preventing misuse. If you execute the PoA while abroad, it must be attested by the Indian embassy or consulate in your country of residence or notarized and apostilled as per The Hague Convention. This step is critical for a smooth and legally sound transaction when buying commercial real estate in India remotely, as it eliminates the need for you to travel for every physical signature.
The Step-by-Step Remote Process for Buying Commercial Real Estate
The entire remote purchasing process can be broken down into three logical phases, each requiring different degrees of professional support. As an investor, your role is primarily to provide strategic direction and final sign-off, relying on your chosen team for on-the-ground execution. This structured approach is the key to successfully acquiring commercial real estate in India.
Phase 1: Market Research and Location Selection
Your remote journey begins with rigorous market research. Commercial property selection is not about emotion; it’s about data. Focus on cities experiencing rapid corporate and infrastructure growth. Prime Tier-1 cities like Mumbai, Delhi-NCR, Bengaluru, and Hyderabad remain the safest bets, but Tier-2 cities such as Pune, Chennai, and Ahmedabad are emerging as high-potential markets offering attractive entry prices and high capital appreciation potential for commercial real estate in India.
Research specific micro-markets within these cities. For office space, look for Grade-A developments in established central business districts (CBDs) or new IT corridors. For retail, focus on high-footfall mall spaces or established high-street locations. Logistics and warehousing thrive near major highways, ports, and industrial hubs. Use online platforms, consult with leading property consultants, and analyze reports from major real estate research firms to define your target investment profile. This initial homework is crucial and forms the investment thesis for your decision to buy commercial real estate in India remotely.
Phase 2: Due Diligence and Title Verification
This is the most critical phase for a remote investor and must be executed by an independent, specialized property lawyer. Never rely solely on the developer’s or seller’s documentation. The goal of this due diligence is to verify the property’s legal standing and ensure it is free from encumbrances.
Key legal checks include:
- Title Verification: Tracing the ownership history (ideally for the last 30 years) to confirm the seller has a clear and marketable title to the property.
- Encumbrance Certificate (EC): Obtaining an EC from the Sub-Registrar’s Office to confirm the property is free from any mortgages, claims, or outstanding liabilities.
- RERA Compliance: For under-construction projects, ensure the developer and project are registered with the respective state’s Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA). RERA registration mandates transparency and protects buyer interests, significantly reducing risk when buying commercial real estate in India remotely.
- Municipal and Building Approvals: Confirming the building plan, occupancy certificate (for ready properties), and land use permits are all in order and comply with local zoning laws.
Simultaneously, you should hire an independent technical valuer for the financial assessment. This professional will audit the construction quality, verify the carpet area, and provide an unbiased valuation report, ensuring you do not overpay for your commercial real estate in India.
Phase 3: Documentation and Registration
Once due diligence is complete and satisfactory, the transaction moves to documentation. Your PoA holder will manage the process in India. First, a detailed Agreement for Sale is drafted, stipulating the final price, payment schedule, project completion timelines, and penalty clauses for non-compliance. Review this document meticulously with your legal counsel before the PoA holder signs it.
The final step is the Property Registration at the local Sub-Registrar’s Office. This legal process transfers the property title to your name. The PoA holder will represent you, pay the requisite stamp duty and registration fees, and submit the necessary documents, including the Sale Deed, identity proofs, and the PoA itself. The registration process legally seals the investment and makes you the rightful owner of the commercial real estate in India. Ensure you receive a certified copy of the registered Sale Deed, which is your ultimate proof of ownership.
Mitigating Risks When Buying Commercial Real Estate in India Remotely

While the rewards are substantial, an astute investor acknowledges and proactively mitigates the inherent risks of remote cross-border transactions. Success in buying commercial real estate in India remotely lies in professional risk management.
The Fraud and Litigation Risk
The most significant risk for an NRI is property fraud, which can involve unclear titles, forged documents, or properties under litigation. The distance makes it difficult to verify documents and ground realities personally.
- Mitigation Strategy: The single most important step is hiring an independent, reputed property lawyer who specializes in NRI/FEMA real estate laws. They must perform the comprehensive 30-year title search and Encumbrance Certificate check in Phase 2. Insist on a legal opinion report that indemnifies their work, providing an extra layer of protection. Never trust a developer-appointed lawyer.
Developer and Project Risk
Developers in India can face financial difficulties, leading to project delays or, worse, stalled projects. For under-construction assets, this risk is magnified.
- Mitigation Strategy: Stick to projects registered under RERA, which mandates developers to deposit 70% of project funds into an escrow account for construction purposes only. Research the developer’s track record extensively: check their completion history, financial stability, and public reputation. Prefer large, established corporate developers known for on-time delivery of commercial real estate in India. Avoid developers with a history of RERA complaints.
Political and Economic Instability
While India’s overall economy is stable, policy changes or sudden shifts in local zoning laws can impact property value and rental demand. Furthermore, currency fluctuation presents a perpetual risk for NRIs.
- Mitigation Strategy: Invest in properties that have already received all necessary permits (Occpancy Certificate or Completion Certificate), thus minimizing regulatory risk. Diversify your investment geographically across different states or cities to hedge against local economic downturns. To counter currency risk, consider that buying commercial real estate in India remotely with a high, stable rental yield in INR will provide a natural hedge, as the rental income can be reinvested in the NRO account or repatriated strategically when the exchange rate is favorable.
The High Rewards: Rental Yields, Appreciation, and Tax Benefits
The successful acquisition of commercial real estate in India is merely the first step. The true value lies in the ongoing income generation and the significant tax benefits available to NRIs.
Unlocking Superior Rental Yields
Commercial properties, such as pre-leased office spaces or high-demand warehouses, are specifically prized for their high and stable returns. A pre-leased property, for example, comes with an existing tenant and a signed long-term lease, ensuring cash flow from day one without any vacancy period risk. These assets typically yield between 8% to 10% annually, sometimes even higher.
The lease structure itself is a reward. Commercial leases are often “triple net” (NNN), meaning the tenant is responsible for property taxes, insurance, and maintenance, shifting the operational burden away from the NRI owner. This structure makes buying commercial real estate in India remotely a truly passive income stream, especially when coupled with a professional property management firm. The consistently strong performance of commercial real estate in India in core metropolitan areas makes this a compelling long-term wealth creation strategy.
Understanding NRI Taxation and DTAA on Commercial Income
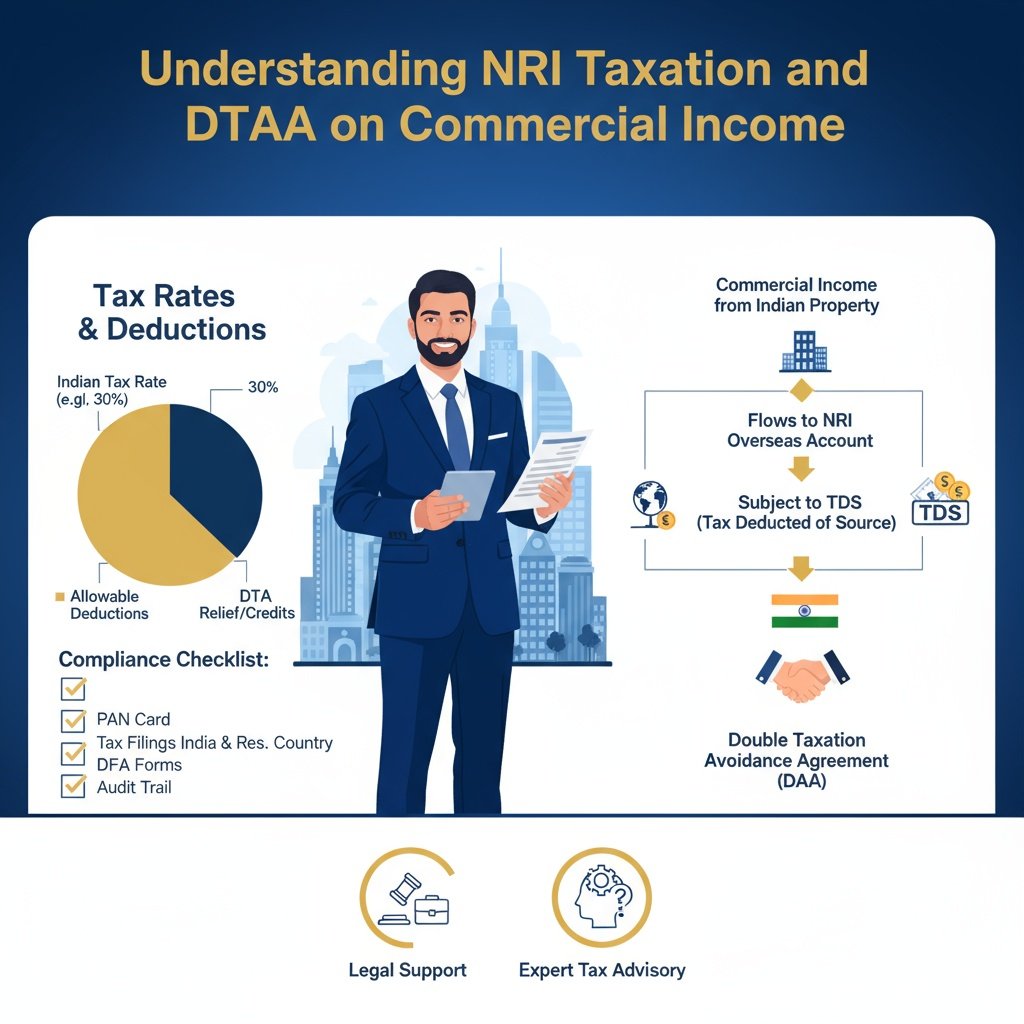
Taxation is a crucial element that impacts your final return on investment (ROI). For NRIs, rental income from commercial real estate in India is taxable in India as per the applicable slab rates. A significant benefit is the standard deduction of 30% on the Gross Annual Value (rental income), which is allowed towards repairs and maintenance, irrespective of actual expenditure. Additionally, interest paid on a commercial property loan is deductible.
When you sell the property, capital gains tax applies. If the property is held for more than 24 months, it is treated as a Long-Term Capital Gain (LTCG) and taxed at a flat rate of 20% with the benefit of indexation, which adjusts the purchase cost for inflation. If sold within 24 months, it is a Short-Term Capital Gain (STCG) and is taxed at your regular slab rate. The buyer of the property is mandated to deduct Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) on the sale proceeds (20% for LTCG, 30% for STCG, plus surcharge and cess). However, the ultimate reward lies in the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) that India holds with over 80 countries. This agreement allows you to claim a tax credit in your country of residence for the taxes already paid in India, ensuring you avoid paying tax on the same income twice. Consulting a tax advisor familiar with both Indian and your country’s tax laws is non-negotiable for maximizing the tax efficiency of your commercial real estate in India investment.
Key Commercial Real Estate Segments for NRI Investment
The Indian commercial market is dynamic, offering multiple avenues for investment based on your risk appetite and capital size. The ideal avenue for buying commercial real estate in India remotely depends on your strategic goals.
- Office Spaces (Grade A): This remains the top choice. Focused on prime business districts (like Bandra-Kurla Complex in Mumbai or Cyber City in Gurugram or Galactic City Plots), these assets attract MNCs and large corporations, ensuring low tenant turnover and high appreciation. Investing in commercial real estate in India of this grade offers maximum security.
- Retail Spaces: High-street retail or prime mall Retail Shop outlets are driven by India’s consumption story. Returns can be higher, but they are also more sensitive to local economic conditions and foot traffic. Look for properties with established, anchor tenants for stability.
- Warehousing and Logistics: Fueled by the e-commerce boom and the ‘Make in India’ initiative, this is a high-growth sector. Large-format warehouses near industrial corridors offer long-term leases to logistics companies and e-commerce giants, providing stable, inflation-linked returns. This is an excellent option for long-term investors buying commercial real estate in India remotely who prefer less operational overhead.
- Fractional Ownership: For investors with a smaller ticket size (typically starting from ₹25 Lakhs), fractional ownership platforms allow pooling capital to purchase a share in a high-value, Grade-A commercial asset. This lowers the entry barrier and provides instant diversification, making high-quality commercial real estate in India accessible to more NRIs.
Finalizing Your Investment: Next Steps and Expert Support
The complexities of FEMA, RERA, and tax regulations necessitate a team approach. Successfully concluding your investment in commercial real estate in India requires reliance on specialized professionals.
Start by assembling your A-Team:
- Specialized NRI Property Lawyer: To conduct independent due diligence, title verification, and process the PoA.
- Chartered Accountant (CA): Essential for tax planning, DTAA benefits, TDS compliance, filing the required Forms 15CA and 15CB for fund repatriation, and ensuring compliance on your commercial real estate in India rental income.
- Property Management Firm (PMF): Crucial for remote investment. A PMF will manage the tenant, collect rent, handle property maintenance, and manage local taxes on your behalf, effectively making your commercial property a hands-off, passive asset.
A thorough exit strategy should be planned from the outset. Understand the market conditions and holding period required to realize long-term capital gains (over 24 months). The entire process, from initial shortlisting to final registration of commercial real estate in India, typically takes 3 to 6 months when executed professionally.
You have the capital and the strategic foresight. Now, act on this opportunity. The window for maximizing the returns on commercial real estate in India is open, but it requires swift, well-informed action.
Contact our sales team for plot details and an exclusive list of pre-leased Grade-A commercial properties in prime business hubs. You are one step away from securing your high-yield, stable commercial real estate in India portfolio.





Join The Discussion